
Everything You’ll Need
| Tool/Material | Laminate Flooring | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Utility Knife | ✔ | Cut underlayment and trim laminate edges |
| Tape Measure | ✔ | Measure room size and plank cuts |
| Straight Edge | ✔ | Make straight cuts and align planks |
| Pry Bar | ✔ | Remove baseboards or old flooring |
| Spacers | ✔ | Keep expansion gaps by walls |
| Tapping Block | ✔ | Tap planks together gently |
| Non-Marring Hammer | ✔ | Use with tapping block for tight fits |
| Laminate Cutter or Saw | ✔ | Cut planks to size |
| Knee Pads | ✔ | Protect knees while working |
| Level | ✔ | Check subfloor and first row are even |
| Chalk Line | ✔ | Mark straight lines |
| Underlayment Roll | ✔ (if needed) | Add cushioning and soundproofing |
| Jigsaw or Oscillating Tool | ✔ | Cut around pipes and door jambs |
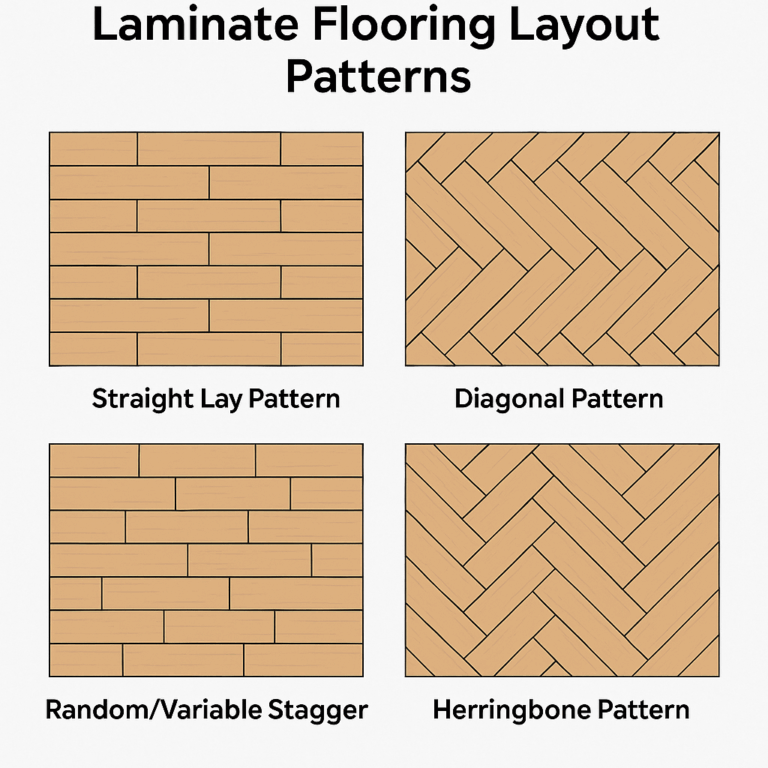
Step 1: Choose a Layout Pattern
Before you install your laminate flooring, think about how you’ll place the planks. Laminate may not have as many pattern choices as vinyl or tile, but your layout can still change how the room looks and feels.
These are the best and most used patterns for laminate flooring:
Straight Lay Pattern (Most Common)
A popular and easy choice.
Planks are set parallel to the longest wall or in the direction of natural light. This gives a clean, classic style and works well in most spaces.
Diagonal Pattern
For a lively, upscale style.
Planks are placed at a 45-degree angle to the walls, making small rooms seem bigger or adding interest to square spaces. Note that this might need more cutting and material.
Random/Variable Stagger
Planks are set in a staggered way, with different plank lengths in each row.
This looks like the natural randomness of hardwood and stops patterns or seams from matching up.
Herringbone or Chevron (Advanced/Pro)
Some special laminate floors are made for herringbone or chevron designs.
These styles are beautiful but need careful cuts and more planning. Not all laminate brands have planks for these patterns.
Step 2: Prepare the Space
Take Off Baseboards and Old Flooring
Begin by removing any baseboards and your old flooring to have a clean, bare surface.
Use a pry bar to gently take off the baseboards — go slowly to avoid damaging the walls so you can reuse the trim later.
If changing carpet, cut it into smaller pieces with a utility knife and pull it up.
For tile, vinyl, or wood, follow the right removal steps for each material.
Clean and Check the Subfloor
Sweep and vacuum well to get rid of dust and dirt.
Look for cracks, dips, or high spots. Use a leveling compound to fill any low areas and sand down any raised spots. A smooth, even subfloor is needed for a long-lasting laminate floor.
Put Down Underlayment
Most laminate floors need an underlayment unless they have one already attached.
Underlayment adds cushioning, cuts down noise, and helps fix small subfloor issues.
Roll it out over the subfloor, ensuring edges touch without overlapping. Tape the seams tightly.
✅ Pro Tip: If putting it over concrete, think about adding a moisture barrier under the underlayment.
Step 3: Choose an Installation Method
Laminate flooring is easy for DIY projects and mainly uses one simple way to install: Click-Lock (Floating Floor). Unlike some floors, laminate usually does not need glue or peel-and-stick.
Click-Lock (Floating Installation)
The Click-Lock system, also known as tongue-and-groove or interlocking, is the most popular and easy option for laminate floors. Each plank’s edges click together, making a strong fit without nails or glue.
This method lets the floor “float” over the subfloor, allowing it to expand and contract naturally with changes in temperature and humidity.
Key Advantages:
- No adhesives required — easy cleanup and fewer materials needed.
- DIY-friendly — ideal for beginners.
- Versatile — works well over different types of subfloors like concrete and plywood.
Installation Tips:
- Leave a 1/4-inch expansion gap around the room using spacers. This stops buckling as the floor expands and contracts.
- Follow the maker’s instructions for lining up planks and clicking them together.
- Use a tapping block and pull bar to make tight seams without damaging the edges.
Step 4: Lay the First Row
Cut the Short Edge of the First Plank
Start by cutting the short edge of your first plank to make it fit better against the wall. Use a utility knife for thinner laminate or a circular saw or miter saw for thicker ones.
Place the First Plank 1/4 Inch from the Wall
Set the first plank next to your starting wall, leaving a 1/4-inch gap between it and the wall. This gap is necessary for the flooring to adjust with temperature and humidity changes.
Use Spacers to Keep the Gap
Put spacers between the wall and the floor to maintain the gap as you lay the floor. Keep using these spacers all around the room.
Stagger End Joints for Stability and Looks
When you begin the second row, cut the first plank so it’s at least 6 inches shorter than the first plank in the previous row. This staggers the joints, making the floor stronger and look more natural.
Tip: Don’t line up joints across rows, as it can weaken the floor and make it look less natural.

Step 5: Cutting Planks to Fit
Straight Cuts — Score and Snap
For straight cuts (like trimming the end of a plank):
Use a utility knife to score along your marked cut line.
Snap the plank along the score for a clean break (this method works best for thinner laminates).
For thicker or tougher laminate, use a laminate cutter, circular saw, or miter saw for precise, clean cuts.
Irregular Cuts — Around Corners and Obstacles
When cutting around door frames, corners, or awkward shapes:
Use a jigsaw or oscillating multi-tool.
These tools allow precise, curved, or angled cuts that a standard saw can’t achieve.
Cutting Around Pipes
Measure the diameter of the pipe and add 1 inch to allow for expansion.
Drill a hole in the plank to fit the pipe size.
Make a straight cut from the hole to the plank’s edge.
Once installed, seal around the pipe with a bead of silicone caulk to cover the gap and prevent moisture from seeping in.
Tight Spaces — Under Door Jambs
Use a jamb saw (also called an undercut saw) to trim the bottom of the door frame.
This allows you to slide the laminate plank neatly underneath for a clean, professional look.
Pro Tip: Always wear safety goggles and work slowly when using power tools to avoid splintering the laminate or damaging surrounding materials.
| Cutting Task | Recommended Tool(s) | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| Straight cuts (length/width) | Utility knife (thin laminate) Laminate cutter or miter saw (standard) | Score and snap for thin laminate Use a saw for clean, straight cuts |
| Irregular cuts (corners, curves) | Jigsaw or oscillating multi-tool | Mark the shape, cut slowly following the line |
| Around pipes | Drill + Jigsaw or Hole saw | Drill a hole + cut a slit to the edge, leave ½” expansion gap |
| Tight spaces (door jambs) | Jamb saw (undercut saw) | Undercut the jamb to slide the plank underneath |
| Final fitting/trimming | Utility knife or laminate cutter | Trim small excess for a snug fit |
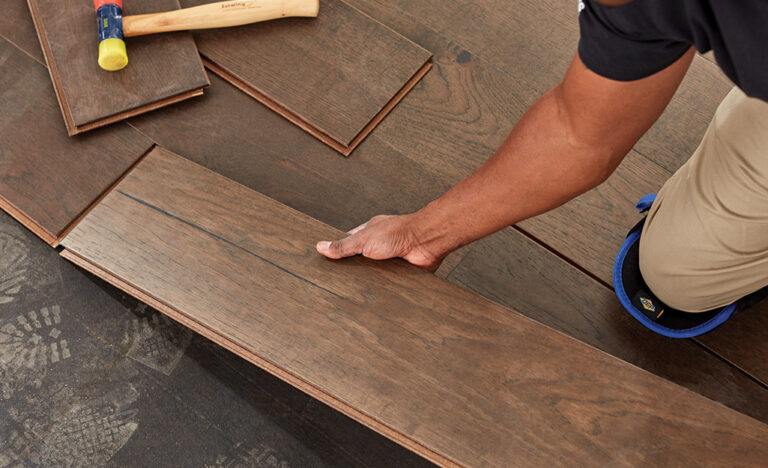
Step 6: Laying Subsequent Rows
Angle the Planks into Place
Begin each new row by angling the tongue of the plank into the groove of the previous row. Gently lower the plank until it clicks or fits snugly into position.
Use a Tapping Block and Non-Marring Hammer
For a tight, seamless fit, use a tapping block and a non-marring hammer (or mallet).
Place the tapping block against the edge of the plank.
Tap gently to close any gaps between the planks.
Never use a standard hammer directly on the laminate—this can chip or damage the edges.
Maintain the Staggered Pattern
Continue staggering the end joints by at least 6 inches in each row for both stability and a natural appearance.
Check Expansion Gaps
Keep spacers along the walls to maintain the 1/4-inch expansion gap throughout the installation.

Step 7: Finishing the Installation
Install Transition Strips
Once all planks are in place, install transition strips at doorways and where the laminate meets other flooring types. These strips:
Provide a smooth, safe transition.
Protect the edges of your laminate flooring.
Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for type and installation.
Transitioning to Other Flooring
Use the right type of transition:
T-molding for floors of equal height.
Reducer strips for transitioning to lower surfaces like tile or vinyl.
Attach transition strips to the subfloor—never directly to the laminate—leaving a 1/4-inch expansion gap to prevent buckling.
Reinstall Baseboards
Reattach baseboards, securing them to the wall, not the floor. This allows the laminate to expand and contract freely beneath.
Allow the Floor to Settle
Before moving furniture back or walking extensively on the floor:
Allow at least 48 hours for the laminate to acclimate to the room’s temperature and humidity.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Installing Laminate Flooring
Installing in High-Moisture Areas
Laminate flooring isn’t recommended for areas with excessive moisture, like full bathrooms or laundry rooms. Water can seep into the seams, causing swelling or warping.
Using a Hammer Directly on Planks
Never use a hammer directly on the laminate. Always use a tapping block or pull bar to gently secure planks without damaging their edges.
Overlapping End Joints
Don’t align or overlap the end joints of planks in adjacent rows. This weakens the floor’s structure and can lead to gaps or uneven surfaces. Stagger the joints by at least 6 inches.
Skipping the Expansion Gap
Failing to leave a 1/4-inch expansion gap around the room’s perimeter can cause buckling as the floor expands and contracts with temperature and humidity changes.
Walking on the Floor Too Soon
Allow the laminate floor to acclimate and settle for 48 hours after installation before subjecting it to foot traffic or placing heavy furniture.
Tips for a Successful Laminate Flooring Installation
- Measure Accurately and Plan for Waste
Measure your room carefully and purchase 10% extra laminate flooring to account for cuts, mistakes, and future repairs. - Inspect Planks Before Installation
Check each plank for defects or damage before laying it. Discard or set aside any damaged pieces to maintain a high-quality finish. - Use Knee Pads for Comfort
Protect your knees by using knee pads, especially during long installation sessions. This can also help you work more efficiently. - Work Methodically and Don’t Rush
Take your time with each step, from laying the first row to cutting planks. Rushing can lead to poor fits, uneven seams, and costly mistakes. - Maintain the Recommended Expansion Gap
Always leave a 1/4-inch expansion gap around the perimeter to prevent buckling as the laminate expands and contracts.
DIY vs. Professional Laminate Flooring Installation
Many homeowners choose laminate flooring because it’s one of the most DIY-friendly flooring options available. But whether to install it yourself or hire a professional depends on your comfort level, tools, and project complexity.
DIY Installation
✅ Pros:
- Save on labor costs (typically $2 to $5 per sq ft).
- Flexibility to work at your own pace.
- Great for smaller, simple rooms.
❌ Cons:
- Requires basic tools (spacers, tapping block, saws).
- Mistakes like improper expansion gaps can lead to warping or separation.
- Time-consuming, especially for larger or irregularly shaped spaces.
Professional Installation
✅ Pros:
- Fast, precise installation.
- Experts handle subfloor prep, tricky cuts, and transitions.
- Often includes a warranty.
❌ Cons:
- Additional cost — typically adds $2 to $5 per sq ft for labor.
On average, laminate flooring installation (materials + labor) costs between $4 and $12 per square foot depending on the style and complexity. For a more detailed breakdown, check out our Laminate Flooring Cost Guide.
| Installation Method | Average Cost per Sq Ft | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| DIY Installation | $1.50 – $4 (materials only) | Save on labor Flexible schedule Good for small areas | Time-consuming Requires tools & skills Mistakes can be costly |
| Professional Installation | $4 – $12 (materials + labor) | Fast & precise Warranty often included Handles complex cuts & transitions | Higher upfront cost |
Do You Need Professional Help With Your Laminate Flooring Installation Project?
Now that you’ve learned how to install laminate flooring, you’re well on your way to creating a stylish, durable floor. But if you’d rather skip the heavy lifting and precise cuts, our expert team is ready to help.
We handle everything — from proper subfloor preparation to perfect plank alignment — so you can sit back and enjoy flawless, long-lasting results. We’ll also assist you in choosing the right laminate style and underlayment to match your space and budget.
Contact us today to schedule your free in-home consultation and see if we serve your area.





